How To Sign Driver Windows 10
By default, all 64-bit Windows versions prevent the installation of devices drivers that are not signed with a valid digital signature. Unsigned drivers are blocked by the operating arrangement. A digital signature ensures that the driver has been released by a trusted developer or vendor, and its code hasn't been modified.
In that location are several ways to disable driver signature verification for the unsigned drivers in Windows (using a GPO, a test boot mode, etc). Today we'll bear witness how to sign whatsoever unsigned commuter for Windows x64 (the guide is applicative for Windows 11, 10, viii.1, and vii).
Contents:
- Create a Self-Signed Commuter Certificate
- Creating a Catalog File (Cat) for Signing a Driver Package
- Signing the Driver Bundle with a Self-Signed Certificate
- Installing a Self-Signed Driver on Windows
- User-Mode and Kernel-Fashion Drivers in Windows
Suppose y'all have a certain unsigned device commuter (without digital signature) for Windows 10 x64. In this instance, it is the driver for a quite old graphics card. The annal with drivers for your Windows version has been downloaded from the vendor's website (I was able to find the video commuter version only for Windows Vista x64) and its contents accept been extracted to the c:\tools\drv1\. Let'south endeavour to install the driver by calculation it to the Windows driver shop with a built-in pnputil tool:
Pnputil –a c:\tools\drv1\xg20gr.inf
Note. This control and all the adjacent ones must exist run in the command prompt as an administrator.
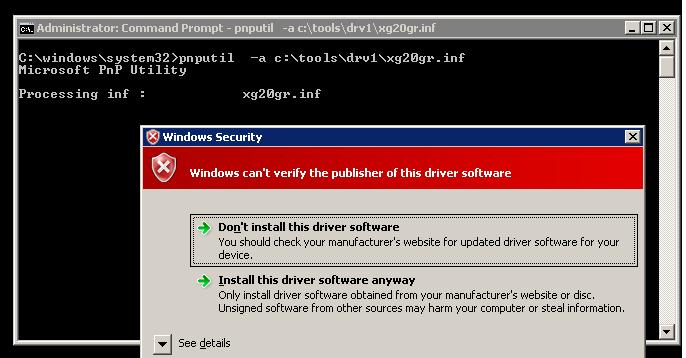
During driver installation, Windows 7 displays a warning that the operating system tin't verify the digital signature of this driver:
Windows can't verify the publisher of this commuter software.
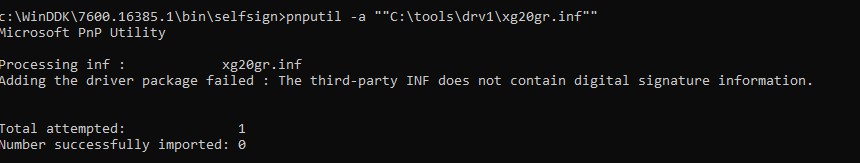
In Windows ten (21H2) this warning doesn't appear, just an error appears in the console:
Processing inf: xg20gr.inf Adding the driver package failed: The third-party INF does not contain digital signature data.
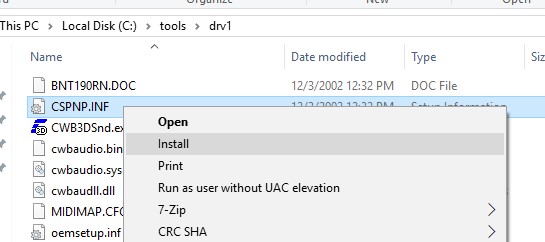
If you right-click on the inf commuter file and select Install when installing a commuter from File Explorer, you receive an fault:
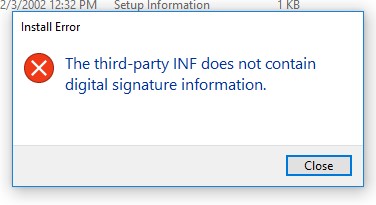
The third-party INF does not contain digital signature data.
Let's try to sign this driver with a self-signed document.
To generate a signature and sign the driver, you need to download and install the following Windows awarding development tools:
- Windows SDK (Software Development Kit) or Microsoft Visual Studio 2005+ for your Windows version. Install the Windows SDK Signing tools for Desktop package which contains the
signtool.exe; - Windows Driver Kit (WDK) — https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/download-the-wdk
Create a Self-Signed Driver Certificate
Create a C:\DriverCert binder at the root of the organisation bulldoze.
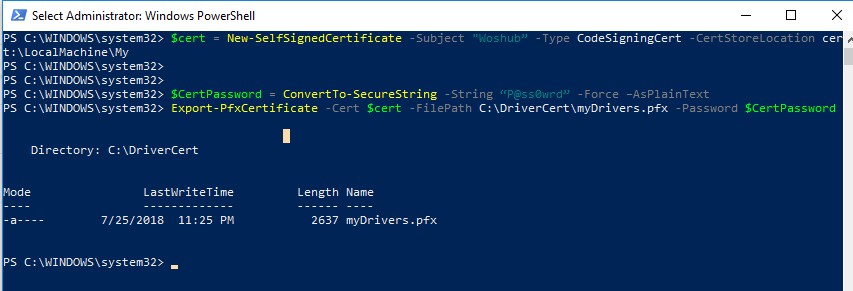
You can use the New-SelfSifgnedCertificate PowerShell cmdlet to create a lawmaking signing document. In this example, we will create a self-signed certificate with a validity period of iii years.
$todaydate = Become-Date
$add3year = $todaydate.AddYears(3)
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject area "WOSHUB" -Type CodeSigningCert -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -notafter $add3year
And then you need to export this certificate to a pfx file with a password:
$CertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "P@ss0wrd" -Force –AsPlainText
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $cert -FilePath C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pfx -Password $CertPassword
Since the certificate we created is self-signed, Windows doesn't trust information technology past default. When yous check the certificate shop with the Sigcheck utility, this certificate will be displayed equally untrusted, because it is not listed in the list of Microsoft Trusted Root Certificates (this listing needs to exist updated periodically).
Now you demand to add the certificate to the Trusted Root store and to the Trusted Publisher certificates:
$certFile = Consign-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath C:\DriverCert\drivecert.cer
Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\AuthRoot -FilePath $certFile.FullName
Import-Document -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\TrustedPublisher -FilePath $certFile.FullName
In previous versions of Windows, y'all must utilize the makecert.exe tool from the Windows Software Evolution Kit (SDK) to generate self-signed certificates. In this case, the commands to create a certificate will expect like this:
cd "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.1\bin"
Create a self-signed certificate and private primal, that is issued, for example, for the company WinOSHub:
makecert -r -sv C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pvk -north CN="WinOSHub" C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.cer
During the creation of the document, the tool will prompt you to specify a password for the central. Permit it be P@ss0wrd.
Create a public key for a publisher certificate (PKSC) we have created earlier:
cert2spc C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.cer C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.spc
Combine the public key (.spc) and the private key (.pvk) in a single certificate file with format Personal Data Exchange (.pfx):
pvk2pfx -pvk C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pvk -pi P@ss0wrd -spc C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.spc -pfx C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pfx -po P@ss0wrd
Add the certificate to trusted:
certmgr.exe -add C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.cer -southward -r localMachine ROOT
certmgr.exe -add C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.cer -s -r localMachine TRUSTEDPUBLISHER
Yous can centrally deploy this document to client computers using Group Policy in an Ad domain.
Open up the machine's local certificate management snap-in (certlm.msc) and verify that your certificate is in the Trusted Publishers and Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
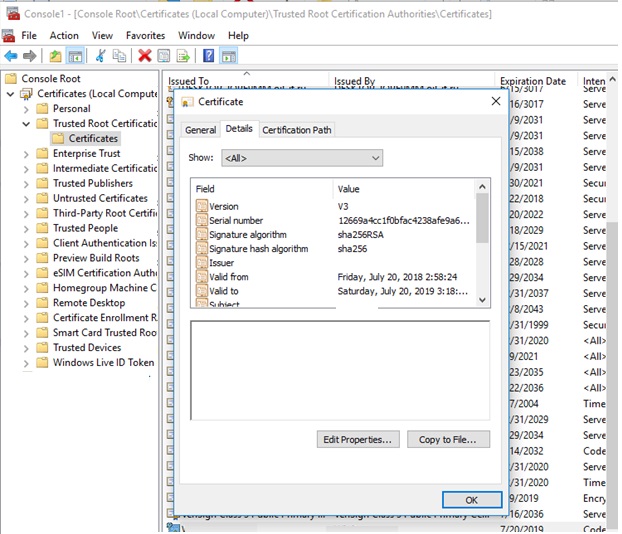
Note. Even though the document has a limited validity period, the expiration of the CodeSigning certificate means that yous can't create new signatures. The validity of the driver already signed by this certificate is unlimited (or onetime signatures are valid during the specified timestamp).
Creating a Catalog File (Cat) for Signing a Driver Parcel
Create the directory C:\DriverCert\xg20 and copy all files from the folder into which the driver from the archive has been originally extracted (c:\tools\drv1\). Make sure that there are files with the extensions .sys and .inf amidst these files (in our example, they are xg20grp.sys and xg20gr.inf).
dr. C:\DriverCert\xg
xcopy c:\tools\drv1\ C:\DriverCert\xg /i /c /k /e /r /y
Become to the directory:
cd "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\ten\bin\10.0.22000.0\x86"
Generate a Cat file (contains data about all the files in the driver package) on the base of operations of the INF file. The inf2cat.exe tool (from the Windows Driver Kit, WDK) allows you to generate a Cat file for your platform:
inf2cat.exe /driver:"C:\DriverCert\xg20" /os:7_X64 /verbose
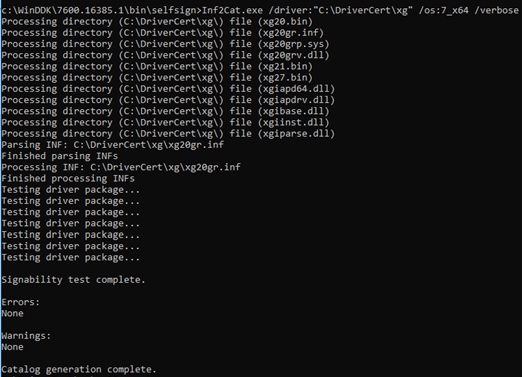
To make sure that the procedure was correct, check that the file C:\DriverCert\xg\xg20gr.true cat has appeared in the target directory, and there are messages in the log:
Signability test consummate.
and
Catalog generation consummate.
Note. In my example the control Inf2Cat.exe returned an mistake:
Signability test failed. Errors: 22.9.7: DriverVer set up to incorrect date (must exist postdated to iv/21/2009 for newest Os) in \hdx861a.inf
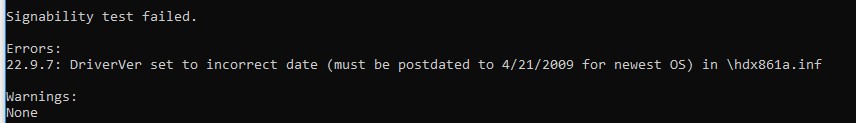
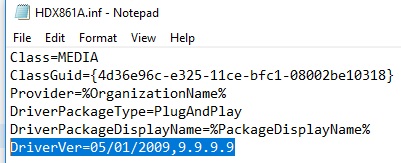
To fix the error, find the line with DriverVer = in the [Version] section and supervene upon information technology with:
DriverVer=05/01/2009,9.9.9.nine
If you lot get an error Missing AMD64 CatalogFile entry (for x64) or Missing 32-fleck CatalogFile entry, then add together the line CatalogFile=xg20gr.cat to the [Version] section of the .inf file.
Signing the Driver Package with a Cocky-Signed Certificate
Go to the following binder:
cd "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22000.0\x64"
Sign the driver packet (ready of files) with the document you have created earlier using Verisign as a timestamp service. The following command will sign the CAT file with a digital signature using a certificate stored in a countersign-protected .pfx file:
signtool sign /f C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pfx /p P@ss0wrd /t http://timestamp.verisign.com/scripts/timstamp.dll /five C:\DriverCert\xg20\xg20gr.cat
On modern versions of Windows 10 and Windows xi, running this control will consequence in an error:
SignTool Error: No file digest algorithm specified. Please specify the assimilate algorithm with the /fd flag. Using /fd SHA256 is recommended and more than secure than SHA1. Calling signtool with /fd sha1 is equivalent to the previous behavior. In social club to select the hash algorithm used in the signing certificate'southward signature, use the /fd certHash option.
Yous demand to use another control:
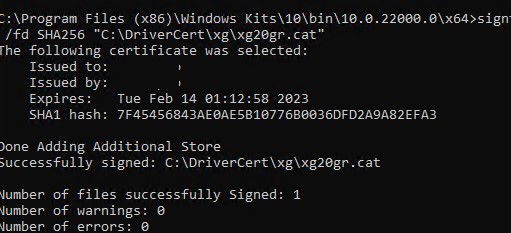
signtool sign /tr http://timestamp.digicert.com /td SHA256 /v /f C:\DriverCert\myDrivers.pfx /p P@ss0wrd "C:\DriverCert\xg\xg20gr.cat"
If the command returns an error SignTool Error: An unexpected internal error has occurred, or Error data: SignerTimeStamp() failed. (-2147012865/0x80072eff), try a different timestamp server URL. Try any of the list:
http://timestamp.comodoca.com/authenticode http://timestamp.globalsign.com/scripts/timstamp.dll http://timestamp.verisign.com/scripts/timstamp.dll http://tsa.starfieldtech.com http://www.startssl.com/timestamp
If the CAT file is signed successfully, the following message should appear:
Successfully signed: C:\DriverCert\xg\xg20gr.cat Number of files successfully Signed: 1
The driver'south digital signature is contained in the .cat file referenced in the .inf file. You tin check the digital signature of the driver in the cat file using the following command:
SignTool verify /v /pa c:\DriverCert\xg\xg20gr.cat
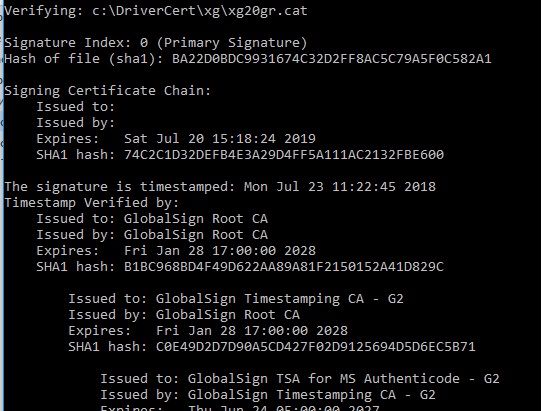
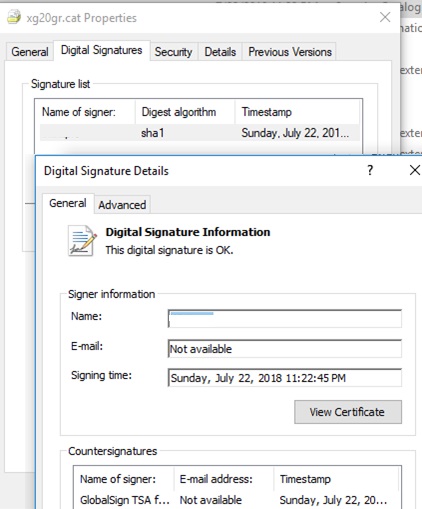
Y'all tin can besides see data about the certificate in the backdrop of the CAT file on the Digital Signatures tab.
If the document is not trusted (or has not been added to the Trusted Root Certificate Store), and then an mistake will appear when running the SignTool verify command:
SignTool Error: A certificate chain candy, merely terminated in a root certificate which is not trusted by the trust provider.
The True cat file contains digital signatures (thumbprints) of all the files that are in the driver directory (files listed in the INF file in the CopyFiles section). If any of these files have been changed, then the checksum of the files will not match the data in the Cat file, and, equally a result, the installation of such a driver volition neglect.
Installing a Self-Signed Driver on Windows
Try to install the commuter we have signed once again using the command:
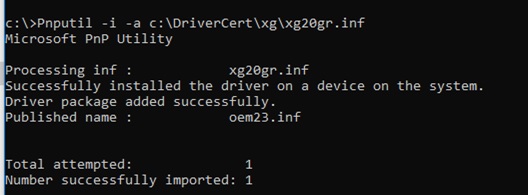
Pnputil –i –a C:\DriverCert\xg20\xg20gr.inf
At present you won't see the warning about the missing digital signature of the commuter.
Successfully installed the driver on a device on the system.
Driver package added successfully.
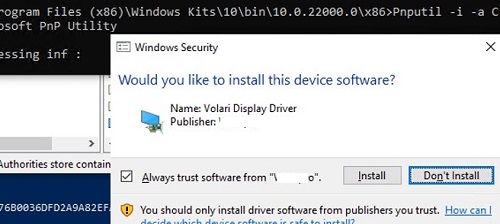
The following warning appears in Windows 10 and 11:
Would you like to install this device software?
Click "Install" to install the driver package on Windows.
If for some reason the driver is not installed, a detailed commuter installation log is contained in the file C:\Windows\inf\setupapi.dev.log. This log file allows you to go more data about the driver installation errors. In most cases, there is a "Driver package failed signature validation" error. Most probable this means that the driver'southward certificate is not added to the trusted certificates shop.
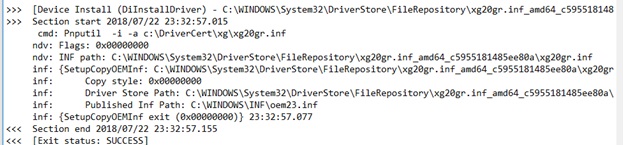
If the driver installation was successful, the setupapi.dev.log file should contain the following lines:
>>> [Device Install (DiInstallDriver) - C:\WINDOWS\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\xg20gr.inf_amd64_c5955181214aa12b\xg20gr.inf] >>> Section kickoff 2018/07/22 23:32:57.015 cmd: Pnputil -i -a c:\DriverCert\xg\xg20gr.inf ndv: Flags: 0x00000000 ndv: INF path: C:\WINDOWS\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\xg20gr.inf_amd64_c5955181214aa12b\xg20gr.inf inf: {SetupCopyOEMInf: C:\WINDOWS\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\xg20gr.inf_amd64_c5955181214aa12b\xg20gr.inf} thirteen:23:37.046 inf: Copy style: 0x00000000 inf: Commuter Shop Path: C:\WINDOWS\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\xg20gr.inf_amd64_c5955181214aa12b\xg20gr.inf inf: Published Inf Path: C:\WINDOWS\INF\oem23.inf inf: {SetupCopyOEMInf exit (0x00000000)} 13:23:37.077 <<< Department end 2018/07/22 xiii:23:37.155 <<< [Exit status: SUCCESS] User-Mode and Kernel-Mode Drivers in Windows
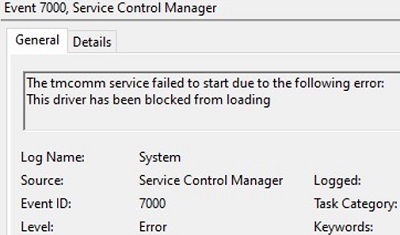
Permit me remind y'all that in Windows the driver can be executed in a kernel-fashion or in a user mode. Kernel-manner drivers signed this way won't load when Windows boots on the UEFI device with Secure Kicking enabled with the fault:
Event ID: 7000 ERROR_DRIVER_BLOCKED 1275 (0x4FB) This driver has been blocked from loading.
You can check if Secure Kick mode is enabled using the PowerShell control:
Confirm-SecureBootUEFI
All kernel-mode drivers loaded with SecureBoot enabled must be signed during the Microsoft certification process (WHQL – Windows Hardware Quality Lab). The reason is that when the kernel is loaded, UEFI cannot verify the certificates in the Windows local auto certificate store.
SignTool Error: Signing Cert does not chain to a Microsoft Code Verification Root.
Microsoft requires mandatory third-party commuter certification under the Windows Hardware Compatibility Program starting with Windows 10 1607.
Self-signed user-mode drivers (normally printers, scanners, plotters, etc.) volition work even with SecureBoot enabled.
For kernel-mode drivers, yous will have to disable digital signature verification and boot Windows in a examination mode with the bcdedit.exe commands:
bcdedit.exe /set /nointegritychecks on
bcdedit.exe /set testsigning ON
Source: http://woshub.com/how-to-sign-an-unsigned-driver-for-windows-7-x64/
Posted by: ellismandred48.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Sign Driver Windows 10"
Post a Comment